Massage Career
There are several benefits to pursuing a career in massage therapy, including:
- Flexibility: Massage therapy careers offer flexible work hours and the ability to work independently or in a spa or clinic setting.
- Personal fulfillment: Massage therapists have the opportunity to help people reduce stress and improve their overall wellness.
- Job growth: The demand for massage therapy services is expected to increase as more people seek alternative forms of health and wellness treatment and more insurance companies cover massage services. Massage therapist job opportunities have risen since the pandemic.
- Competitive earnings: Massage therapists can earn a good income, with the potential for higher earnings with experience and specialization.
- Professional development: Massage therapists have opportunities for continuing education and professional development to enhance their skills and stay current in the field.
Overall, a career in massage therapy can offer a rewarding and fulfilling work-life balance for individuals who are passionate about helping others and promoting wellness. Few professions are as easy to travel with, pay as much per hour, provide as much scheduling flexibility, and result in as many happy clients.

Massage Styles and Modalities
There are literally hundreds of massage therapy modalities in existence, and most massage schools teach primarily swedish-style massage. PCAB offers professional instruction in standard bodywork modalities such as Swedish, Lomilomi, Shiatsu, and Thai massage, and our focus is primarily on slow-movement, deep-listening therapies that are based on the latest (neuro)science of touch and interoception. The “best” style of massage is the one that is the most effective for meeting the client’s biological and psychological needs as well as fitting your preferences for the types of issues you want to focus on, how you prefer to move during a massage, and what your career goals are. Ultimately, there are only so many ways to touch the body, so while we teach separate modalities, our emphasis is to make you skillful in a broad variety of touch styles so that you can apply them in a customized manner that is most appropriate for exploring your client’s goals
Massage Licensing
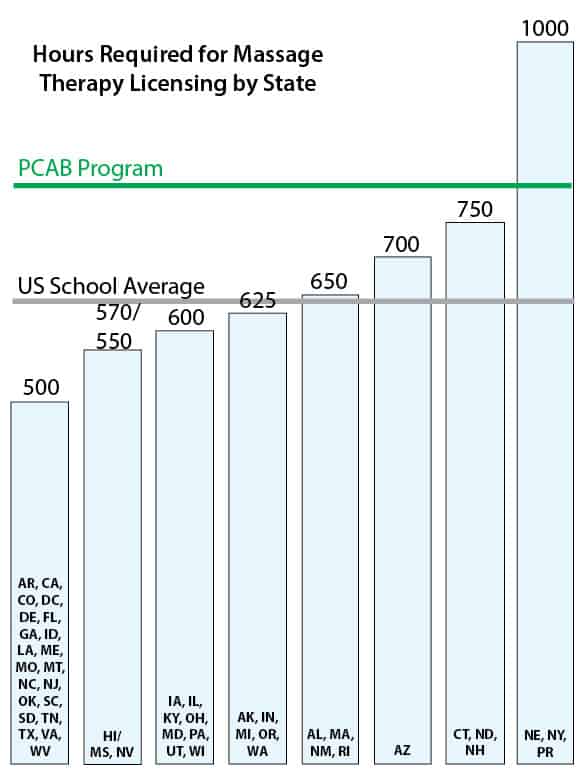
The vast majority of US States and Canadian provinces require that massage therapists be licensed in order to practice massage therapy as a paid profession, and the requirements for each state are different. Most states require a minimum of 500 hours of training. One highly respected guideline (the Entry-Level Massage Education Blueprint) recommends a core curriculum of 625 hours. The average massage therapy training in the US is between 642 and 697 hours.
Most states (except Hawaii) that license massage therapists require a passing score on the Massage & Bodywork Licensing Exam (MBLEx) or one of two exams formerly (no longer) provided by the National Certification Board for Therapeutic Massage & Bodywork (NCBTMB), and maintaining a license in most of those states requires continuing education hours. This exam only needs to be passed once, and then the passing score can be used for licensing in all states that require it. PCAB graduates have a consistently higher pass rate than the national average. For 2021 and 2022, PCAB graduates had a 100% pass rate, compared to the 70% national average during that period. One can signup for the MBLEx exam on the website for the Federation of State Massage Therapy Boards.
In Hawaii, which does it differently than most states, one needs 570 hours of coursework in massage in order to qualify to sit for Hawaii’s own exam. Once this exam is passed, one only needs to pay the license renewal fee and submit 12 hours of CE credits every two years. Massage trainings in Hawaii are approved through one of two routes: either Apprentice Programs approved by the Department of Commerce and Consumer Affairs (most common) or Massage Schools through the Hawaii Department of Education (which is what PCAB utilizes). Only those approved by the DOE are allowed to call themselves schools, and these programs are the ones most similar to programs on the mainland since most of the hours are in a classroom setting, not in an apprenticeship setting (which is unique to Hawaii). Note that many states (including CA and WA) do not accept hours from apprentice programs, so if one wants to be licensed outside of Hawaii, one needs to attend a DOE-licensed school such as PCAB.
The program at PCAB meets or exceeds the hour requirements for most states (except NE and NY). This means that the hours acquired at PCAB can be transferred to your state so you can qualify for licensing in those states. Most of our students who are now licensed massage therapists are from the states of HI, AK, WA, OR, CA, CO, NM, TX, MA, PA, NC, and FL–hotlinks take you to the state’s massage licensing webpage. See the table below for a quick reference for licensing in some states:
| State | Hours | CPR | First Aid | Background /fingerprints |
Exam | URL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hawaii | 570 | yes | Hawaii | URL | ||
| Alaska | 625 | yes | yes | MBLEx/NCBTMB | URL | |
| Washington | 625 | yes | yes | MBLEx/NCBTMB | URL | |
| Oregon | 625 | yes | yes | MBLEx/NCBTMB | URL | |
| California | 500 | yes | see CAMTC website | URL | ||
| Colorado | 500 | yes | MBLEx/NCBTMB | URL | ||
| New Mexico | 650 | yes | yes | yes | MBLEx/NCBTMB | URL |
| Texas | 500 | yes | MBLEx/NCBTMB | URL | ||
| Tennessee | 500 | yes | yes | MBLEx/NCBTMB | URL | |
| Michigan | 500 | yes | yes | MBLEx/NCBTMB | URL | |
| Massachusetts | 650 | none | URL | |||
| Pennsylvania | 600 | yes | MBLEx/NCBTMB | URL | ||
| North Carolina | 500 | yes | MBLEx/NCBTMB | URL | ||
| Florida | 500 | no | no | yes | MBLEx/NCBTMB | URL |
If you have any questions about licensing, please contact us.
Please be sure to also check out our pages on
- How Massage Therapy Works
- Ultimate Guide on Getting a Massage Therapy License
- Massage Resources (websites, books, articles, etc.)